Tidy summarizes information about the components of a model. A model component might be a single term in a regression, a single hypothesis, a cluster, or a class. Exactly what tidy considers to be a model component varies across models but is usually self-evident. If a model has several distinct types of components, you will need to specify which components to return.
Usage
# S3 method for class 'nlrq'
augment(x, data = NULL, newdata = NULL, ...)Arguments
- x
A
nlrqobject returned fromquantreg::nlrq().- data
A base::data.frame or
tibble::tibble()containing the original data that was used to produce the objectx. Defaults tostats::model.frame(x)so thataugment(my_fit)returns the augmented original data. Do not pass new data to thedataargument. Augment will report information such as influence and cooks distance for data passed to thedataargument. These measures are only defined for the original training data.- newdata
A
base::data.frame()ortibble::tibble()containing all the original predictors used to createx. Defaults toNULL, indicating that nothing has been passed tonewdata. Ifnewdatais specified, thedataargument will be ignored.- ...
Additional arguments. Not used. Needed to match generic signature only. Cautionary note: Misspelled arguments will be absorbed in
..., where they will be ignored. If the misspelled argument has a default value, the default value will be used. For example, if you passconf.lvel = 0.9, all computation will proceed usingconf.level = 0.95. Two exceptions here are:
See also
Other quantreg tidiers:
augment.rq(),
augment.rqs(),
glance.nlrq(),
glance.rq(),
tidy.nlrq(),
tidy.rq(),
tidy.rqs()
Examples
# fit model
n <- nls(mpg ~ k * e^wt, data = mtcars, start = list(k = 1, e = 2))
# summarize model fit with tidiers + visualization
tidy(n)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 5
#> term estimate std.error statistic p.value
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 k 49.7 3.79 13.1 5.96e-14
#> 2 e 0.746 0.0199 37.5 8.86e-27
augment(n)
#> # A tibble: 32 × 4
#> mpg wt .fitted .resid
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 21 2.62 23.0 -2.01
#> 2 21 2.88 21.4 -0.352
#> 3 22.8 2.32 25.1 -2.33
#> 4 21.4 3.22 19.3 2.08
#> 5 18.7 3.44 18.1 0.611
#> 6 18.1 3.46 18.0 0.117
#> 7 14.3 3.57 17.4 -3.11
#> 8 24.4 3.19 19.5 4.93
#> 9 22.8 3.15 19.7 3.10
#> 10 19.2 3.44 18.1 1.11
#> # ℹ 22 more rows
glance(n)
#> # A tibble: 1 × 9
#> sigma isConv finTol logLik AIC BIC deviance df.residual nobs
#> <dbl> <lgl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int>
#> 1 2.67 TRUE 0.00000204 -75.8 158. 162. 214. 30 32
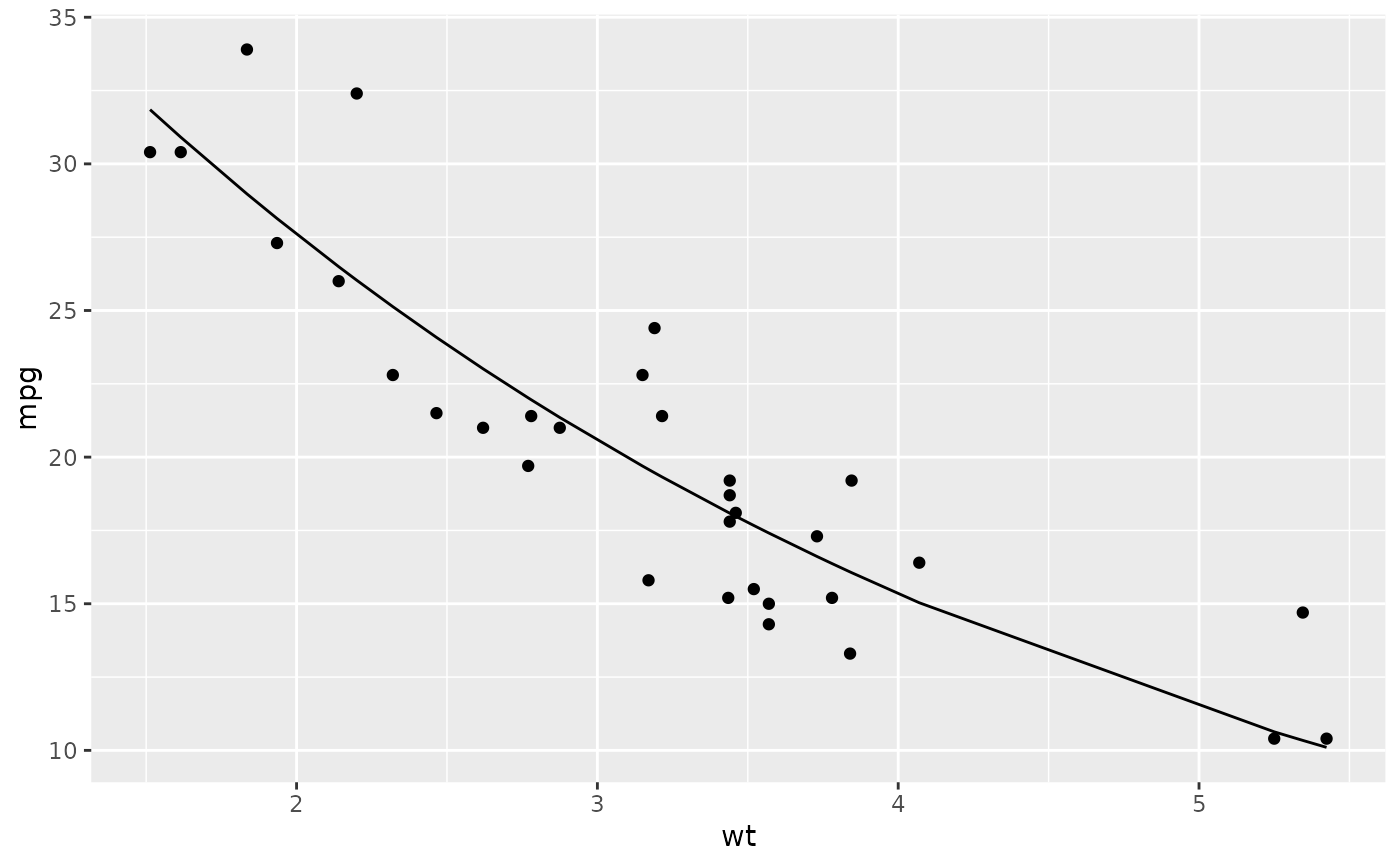
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(augment(n), aes(wt, mpg)) +
geom_point() +
geom_line(aes(y = .fitted))
 newdata <- head(mtcars)
newdata$wt <- newdata$wt + 1
augment(n, newdata = newdata)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 13
#> .rownames mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.62 16.5 0 1 4
#> 2 Mazda RX… 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.88 17.0 0 1 4
#> 3 Datsun 7… 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 3.32 18.6 1 1 4
#> 4 Hornet 4… 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 4.22 19.4 1 0 3
#> 5 Hornet S… 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 4.44 17.0 0 0 3
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 4.46 20.2 1 0 3
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: carb <dbl>, .fitted <dbl>
newdata <- head(mtcars)
newdata$wt <- newdata$wt + 1
augment(n, newdata = newdata)
#> # A tibble: 6 × 13
#> .rownames mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Mazda RX4 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.62 16.5 0 1 4
#> 2 Mazda RX… 21 6 160 110 3.9 3.88 17.0 0 1 4
#> 3 Datsun 7… 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 3.32 18.6 1 1 4
#> 4 Hornet 4… 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 4.22 19.4 1 0 3
#> 5 Hornet S… 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 4.44 17.0 0 0 3
#> 6 Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 4.46 20.2 1 0 3
#> # ℹ 2 more variables: carb <dbl>, .fitted <dbl>
